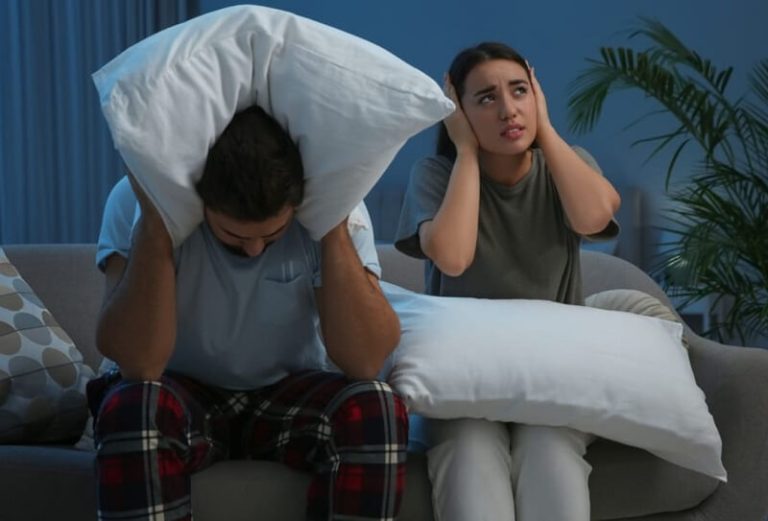
In today’s increasingly noisy world, effective noise control is crucial for creating comfortable and productive spaces, whether at home, in the office, or on the road. Excessive noise can negatively impact sleep, concentration, productivity, and overall well-being. Understanding the difference between soundproofing and sound deadening is the first step toward achieving a quieter and more peaceful environment.
This article explores the distinctions between these two methods, examining their unique benefits, applications, and materials to help you make informed decisions for your specific needs.
Defining Soundproofing and Sound Deadening
What is Soundproofing?
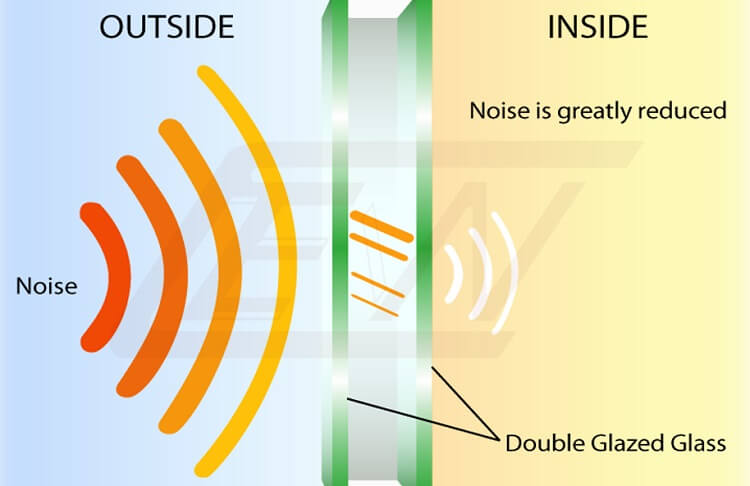
Soundproofing aims to significantly reduce the transmission of sound between spaces. It involves creating barriers that obstruct the passage of sound waves, minimizing the amount of noise that enters or escapes a room or vehicle. While complete sound elimination is practically impossible, effective soundproofing can dramatically reduce noise levels and enhance privacy.
How It Works
Soundproofing relies on principles of mass, absorption, and decoupling.
Dense materials like Mass Loaded Vinyl (MLV) add mass to surfaces, making it harder for sound waves to penetrate. Multiple layers of materials and air gaps further disrupt sound transmission. Sealing gaps and cracks with acoustic caulk prevents sound leakage.
Specialized techniques like decoupling, using resilient channels or sound isolation clips, minimize the transfer of vibrations through structural elements.
What is Sound Deadening?
Sound deadening, also known as sound absorption or damping, focuses on improving the acoustic quality within a space by minimizing reflections, echoes, and reverberations. It does not necessarily block sound from entering or exiting but controls how sound behaves within the enclosed area. This is particularly useful in environments like home theaters, recording studios, or even vehicles where clear sound reproduction is desired.
How It Works
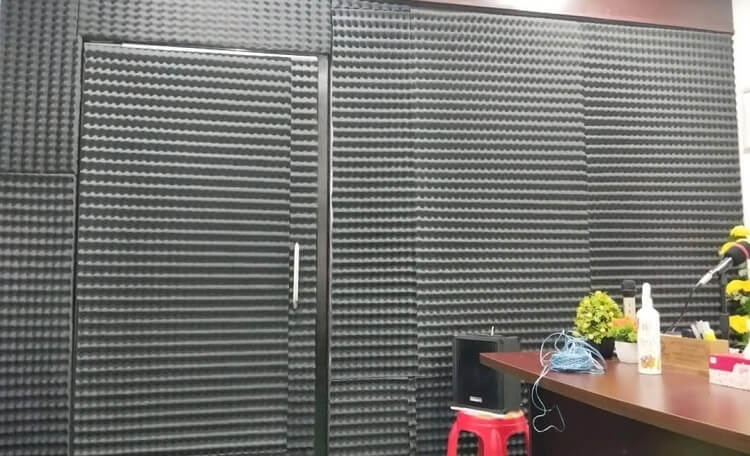
Sound deadening utilizes absorbent materials like acoustic foam, sound mats, and soft furnishings to absorb sound waves and convert their energy into heat.
This reduces the amount of sound that bounces off surfaces, leading to a clearer, more controlled acoustic environment. Different materials are effective at absorbing different frequencies of sound, allowing for customized solutions depending on the specific noise issues.
Core Differences Between Soundproofing and Sound Deadening
What is the difference between soundproofing and sound deadening? The table below summarizes the core distinctions:
| Feature | Soundproofing | Sound Deadening |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Reduces sound transmission between spaces | Improves sound quality within a space |
| Method | Blocks sound waves | Absorbs sound waves |
| Materials | MLV, Drywall, Acoustic Caulk, Resilient Channels | Acoustic Foam, Sound Mats, Carpets, Curtains |
| Effect | Quieter environment, increased privacy | Reduced echoes, clearer sound |
Techniques for Soundproofing
Adding Mass
Increasing the density of walls, ceilings, and floors using materials like MLV or double drywall impedes sound wave penetration.
The heavier the surface, the less it vibrates and transmits sound.
Sealing Gaps
Meticulously sealing gaps around windows, doors, and electrical outlets with acoustic caulk or weatherstripping is crucial for effective soundproofing. Even small gaps can significantly compromise noise reduction efforts.
Decoupling Structures
Decoupling techniques, such as installing resilient channels or sound isolation clips, separate structural layers (e.g., drywall from studs), minimizing vibration transfer and reducing sound transmission.
Techniques for Sound Deadening
Absorbing Sound
Strategic placement of acoustic foam panels, especially in areas where sound reflections are prominent, effectively captures and absorbs sound waves, minimizing echoes and improving clarity.
Dampening Vibrations
Applying sound-dampening mats or sprays to vibrating surfaces, such as car doors or appliance panels, reduces noise generated by vibrations. This is especially helpful for low-frequency noise.
Using Soft Furnishings
Incorporating soft furnishings like thick carpets, heavy curtains, and upholstered furniture naturally absorbs sound waves, contributing to a quieter and more acoustically pleasing environment.
Real-Life Applications: Soundproofing vs.
Sound Deadening
Home Theater
Soundproofing: Install double-glazed windows and dense walls to minimize noise intrusion from outside, ensuring an immersive movie experience.
Sound Deadening: Place acoustic panels on walls and ceilings, use thick carpets, and consider bass traps to control low-frequency sounds and optimize sound quality within the room.
Vehicle Noise Control
Soundproofing: Apply MLV sheets to car doors, floor, and roof to block road noise.
Sound Deadening: Add vibration-dampening mats to the floor, doors, and trunk to reduce engine and tire noise, creating a quieter ride.
Office Spaces
Soundproofing: Construct walls with sound-dampening materials and install solid-core doors to enhance privacy and minimize distractions between offices.
Sound Deadening: Use fabric-wrapped acoustic panels, carpets, and sound-absorbing ceiling tiles to reduce echoes and reverberations, improving speech intelligibility and creating a more comfortable workspace.
FAQ
Can soundproofing and sound deadening be used together?
Yes, combining soundproofing and sound deadening provides a comprehensive approach to noise control. Soundproofing minimizes noise transmission between spaces, while sound deadening optimizes the acoustic environment within a space. This combination creates a quiet and acoustically pleasing environment.
Which method is more cost-effective for small spaces?
Sound deadening is generally more budget-friendly for small spaces, as it often involves adding absorptive materials rather than extensive structural modifications.
Do soundproofing materials also deaden sound?
Some soundproofing materials, like thick curtains or acoustic panels, can have sound-deadening properties, but their primary function is to block sound transmission.
Dedicated sound-deadening materials are typically more effective at absorbing sound within a space.
Is professional installation necessary for soundproofing?
While some sound deadening solutions are DIY-friendly, professional installation is often recommended for optimal soundproofing results, especially for complex projects or when dealing with significant noise issues. Soundproofing can be a worthwhile investment for achieving a quieter environment.
Conclusion
Soundproofing and sound deadening are distinct yet complementary approaches to noise control. By understanding their differences and how they work, you can choose the right methods or combine them strategically to achieve your desired acoustic environment. Whether you’re aiming to create a peaceful home theater, a productive office, or a quiet vehicle, careful consideration of soundproofing and sound deadening techniques can dramatically enhance your comfort and well-being.
If you’re facing complex noise challenges or unsure about the best approach, consult with an acoustics professional for personalized advice and guidance.