Noise management is crucial for creating productive and comfortable environments, whether in a bustling office or the tranquility of your home. When it comes to noise control, two prominent solutions often come up: sound masking and soundproofing. Understanding the distinction between sound masking vs soundproofing is paramount for selecting the most effective approach for your specific needs.
While both aim to improve the acoustic environment, they achieve this through different mechanisms. Sound masking utilizes carefully engineered background noise to reduce the perception of distracting sounds, while soundproofing physically blocks or reduces sound transmission between spaces. This article explores the nuances of each method, empowering you to make an informed decision for optimizing your acoustic environment.
What Is Sound Masking?
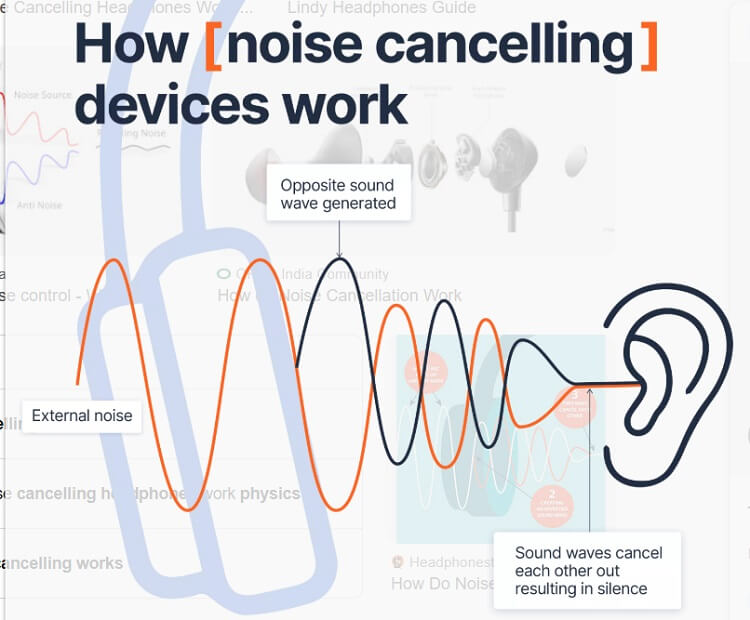
Sound masking is a technology that introduces a controlled, ambient background sound to reduce the perception of unwanted noises.
It doesn’t eliminate the noise itself, but rather makes it less noticeable and distracting. Think of it like adding a subtle layer of sound that covers up other intrusive sounds.
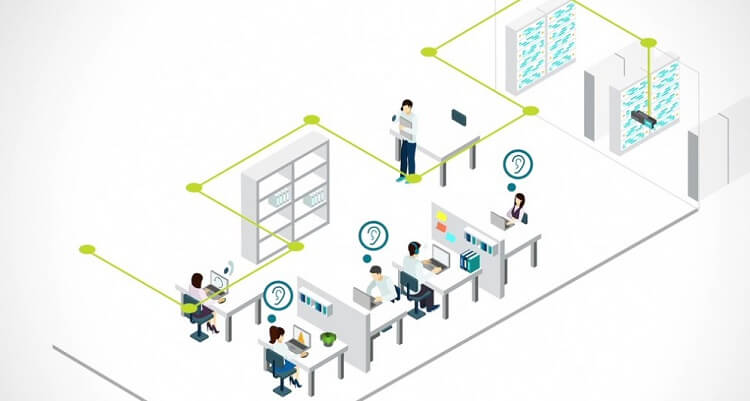
How It Works: Specialized devices called sound maskers emit a carefully engineered sound, often described as similar to airflow or white noise, although more sophisticated systems utilize a range of frequencies tailored to the specific environment. This engineered sound is distributed evenly throughout the space through strategically placed speakers, raising the ambient noise floor and making conversations and other disruptive sounds less intelligible.
Various types of sound masking exist, utilizing different frequency spectrums:
- White Noise: Contains equal energy across all audible frequencies, often perceived as a hissing sound.
- Pink Noise: Has more energy in lower frequencies, offering a more balanced and less harsh sound than white noise.
Applications: Sound masking is frequently employed in open offices, healthcare facilities, libraries, and other shared environments where speech privacy and concentration are essential.
Benefits: Sound masking is a relatively affordable and easy-to-implement solution. It can significantly improve focus and productivity in open workspaces and enhance privacy in areas where confidential conversations occur.
For instance, in a bustling office, sound masking can make conversations in adjacent cubicles less audible, improving speech privacy without requiring physical modifications to the office layout.
What Is Soundproofing?
Soundproofing, unlike sound masking, focuses on physically blocking or absorbing sound waves to prevent them from traveling between spaces. This involves adding barriers and materials that disrupt the transmission of sound.
How It Works: Soundproofing utilizes various materials and techniques to minimize sound transmission.
These include:
- Absorption: Materials like acoustic panels, foam insulation, and heavy curtains absorb sound energy, reducing reflections and reverberations.
- Decoupling: Creating air gaps or using resilient channels in walls and ceilings disrupts the path of sound vibrations.
- Adding Mass: Dense materials like concrete, drywall, and specialized soundproofing composites block sound transmission more effectively than lighter materials.
Common soundproofing materials are assigned a Sound Transmission Class (STC) rating, indicating their effectiveness in blocking sound. Higher STC ratings signify better sound insulation.
Applications: Soundproofing is commonly used in recording studios, home theaters, residential buildings near airports or busy roads, and any space where minimizing external noise intrusion is crucial.
Benefits: Soundproofing creates quieter environments by effectively eliminating external noise and containing sound within a specific area. It enhances sound quality within spaces by minimizing unwanted reflections and reverberations. For more detailed information on reflection, absorption, and transmission of sound, you can explore further.
Unlike sound masking, soundproofing often requires structural modifications and is typically more expensive to implement. For tips on effectively soundproofing a living room, check out this guide on soundproofing a living room.
Core Differences Between Sound Masking and Soundproofing
| Feature | Sound Masking | Soundproofing |
|---|---|---|
| Purpose | Reduces the perception of sound, making it less intrusive. | Physically blocks or absorbs sound transmission. |
| Implementation | Installation of electronic sound masking systems. | Use of construction materials and techniques (insulation, acoustic panels, etc.). |
| Effectiveness | Effective for improving speech privacy and reducing distractions. | Ideal for blocking external noises and isolating sound within a room. |
| Cost | Generally more affordable. | Higher upfront costs due to materials and labor. |
Pros and Cons of Sound Masking
Pros
- Affordable and easy to install.
- Improves focus and concentration in shared environments.
- Flexible and adjustable to different settings.
Cons
- Ineffective at blocking loud or persistent noises.
- Limited to managing noise perception rather than eliminating it.
- May not be suitable for all individuals (some may find the masking sound distracting).
Pros and Cons of Soundproofing
Pros
- Effectively blocks unwanted noise from entering or leaving a space.
- Enhances sound quality within a room.
- Durable and long-lasting solution.
Cons
- Expensive and labor-intensive to install.
- Less adaptable once installed.
- Can require significant structural modifications. For information on soundproofing thin walls in apartments, refer to this guide.
Choosing Between Sound Masking and Soundproofing
The best choice between sound masking and soundproofing depends on your specific needs and goals.
Consider the following:
- For Privacy and Focus in Shared Spaces: Sound masking is often the ideal choice for open-plan offices, call centers, and healthcare facilities where speech privacy and reduced distractions are priorities.
- For Noise Elimination and Isolation: Soundproofing is the best solution for rooms requiring quiet, such as recording studios, home theaters, or bedrooms near noisy streets.
- Hybrid Approach: In some cases, combining both methods delivers optimal results. For example, a conference room might benefit from both soundproofing to block external noise and sound masking to ensure speech privacy within the room.
Consulting with an acoustics professional can help you determine the most appropriate solution based on your individual circumstances and budget.
FAQ
What is the primary difference between sound masking and soundproofing?
Sound masking adds background noise to reduce the perception of distracting sounds, while soundproofing physically blocks or absorbs sound transmission.
Can sound masking and soundproofing be used together?
Yes, combining these methods can provide comprehensive noise management in environments requiring both sound isolation and speech privacy.
Which method is more cost-effective?
Sound masking is typically more affordable and easier to install than soundproofing. Soundproofing often involves more significant material and labor costs.
Conclusion
Effective noise management is essential for creating comfortable and productive spaces. Both sound masking and soundproofing play valuable roles in achieving this, but they address noise issues through different approaches.
By understanding the distinctions between sound masking vs soundproofing, their respective strengths and weaknesses, and the factors influencing your choice, you can implement the most effective strategy for optimizing your acoustic environment.
Whether your goal is to enhance privacy, minimize distractions, or block unwanted noise, careful consideration of these methods will help you create the ideal soundscape for your specific needs. Contacting a qualified acoustics consultant can provide tailored recommendations and ensure optimal results.