The relentless hum of traffic, the chatter of coworkers, the drone of airplane engines—modern life is saturated with noise that disrupts focus, hinders productivity, and elevates stress. If you’re seeking tranquility in this cacophony, understanding how electronic noise cancellation (ENC) works can be your key to a quieter world. ENC technology actively combats unwanted sounds, transforming noisy environments into havens of peace and focus, whether you’re in a bustling office, a crowded airplane, or simply trying to relax at home.
What Is Electronic Noise Cancellation?
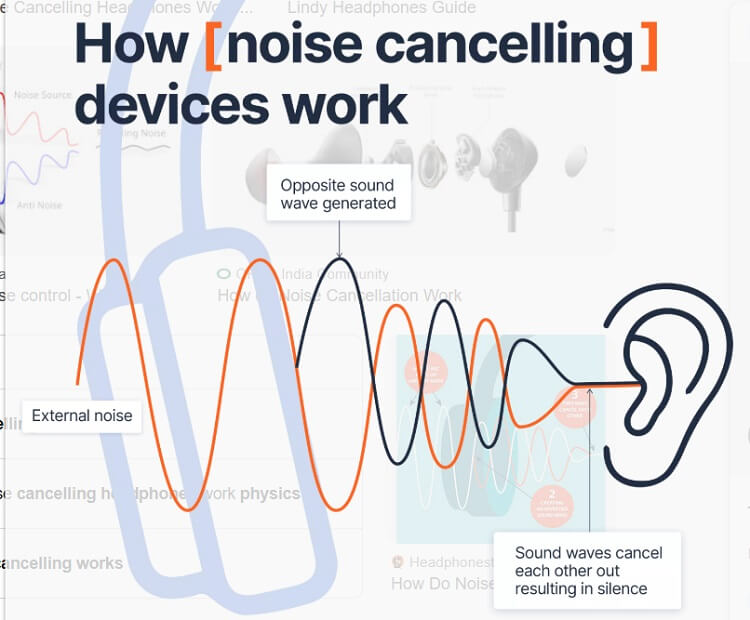
Electronic noise cancellation (ENC) is a sophisticated technology that actively reduces unwanted sound by generating opposing sound waves.
Unlike passive noise isolation, which relies on physical barriers like foam or earplugs to muffle sound, ENC uses digital signal processing (DSP) to analyze and neutralize ambient noise in real time. This proactive approach makes it significantly more effective at reducing unwanted sounds, especially consistent low-frequency noises.
Key Features of ENC:
- Active Noise Control: ENC utilizes microphones and processors to detect and cancel ambient sounds. This active approach distinguishes it from passive noise reduction.
- Real-Time Processing: ENC constantly analyzes and adapts to changing noise levels, creating a consistently quiet experience—the “seamless” aspect of the technology comes from this continuous adaptation.
The system dynamically adjusts the anti-noise signal to match the fluctuating ambient noise.
- Wide Applications: ENC technology is integrated into a diverse range of products, from headphones and earbuds to vehicles, smartphones, smart home devices, and even industrial equipment.
Imagine sitting on a crowded bus, yet being able to clearly hear your podcast without increasing the volume—that’s the power of ENC.
How Does Electronic Noise Cancellation Work?
How does electronic noise cancellation work? The process unfolds in four key steps, utilizing microphones, a digital signal processor, and the generation of “anti-noise” to neutralize unwanted sounds.
Step 1: Detecting Ambient Noise
ENC-enabled devices use built-in microphones to capture surrounding environmental sounds. These microphones are strategically positioned to effectively pick up the unwanted noise frequencies, such as the drone of an airplane engine, the hum of an air conditioner, or the general background chatter in a cafe.
Step 2: Analyzing Noise Patterns
A specialized Digital Signal Processor (DSP) analyzes the captured noise.
This analysis goes beyond simply registering the presence of sound; the DSP meticulously identifies the frequency, amplitude, and waveform of the noise to create a precise counteracting wave. This detailed analysis is crucial for effective noise cancellation.
Step 3: Generating Anti-Noise
Based on the analysis, the DSP creates an “anti-noise” wave. This wave is a mirror image of the unwanted noise—identical in frequency but 180 degrees out of phase (inverted).
When the original noise and the anti-noise wave meet, they cancel each other out through a phenomenon called destructive interference. This occurs because the peaks of one wave align perfectly with the troughs of the other, effectively neutralizing the overall sound.
Step 4: Emitting Anti-Noise
The device’s speakers emit the precisely engineered anti-noise wave. This wave meets the incoming noise before it reaches the user’s ears, effectively neutralizing the unwanted sound.
The entire process, from detection to emission of the anti-noise, happens in milliseconds, creating a seamless and continuous reduction in perceived noise.
Real-World Example
The hushed tranquility experienced in high-end noise-canceling headphones on an airplane perfectly illustrates ENC in action. The constant drone of the engines fades into the background, allowing for a peaceful and immersive listening experience.
Types of Electronic Noise Cancellation
There are three main types of ENC, each with its own strengths and weaknesses:
1. Feedforward ENC
- How It Works: Uses microphones placed outside the earcup (or speaker enclosure) to detect noise before it reaches the ear.
- Advantages: Particularly effective for consistent, predictable noises.
- Limitations: Can struggle with sudden, unexpected noise changes.
2. Feedback ENC
- How It Works: Utilizes microphones placed inside the earcup (or speaker enclosure) to monitor and adjust noise cancellation in real time.
- Advantages: Adapts well to dynamic sound environments.
- Limitations: Can sometimes slightly impact audio quality due to the microphone placement.
3. Hybrid ENC
- How It Works: Combines both feedforward and feedback ENC for superior noise cancellation.
- Advantages: Provides the best performance across a wide range of settings.
- Applications: Commonly found in high-end headphones and automotive systems.
Benefits of Electronic Noise Cancellation
Enhanced Focus & Productivity
Studies have shown that reducing background noise can significantly improve focus and productivity. One study indicated a potential increase in productivity of up to 66% in office environments with reduced noise levels.
ENC creates a personal oasis of quiet, allowing for deeper concentration during work or study.
Improved Audio Quality
By minimizing background interference, ENC enhances audio quality for both music and calls. This clear audio is especially beneficial for remote workers and frequent travelers who rely on virtual meetings and conference calls.
Health Benefits
Prolonged exposure to excessive noise can contribute to stress, fatigue, and sleep disturbances. The World Health Organization (WHO) has linked noise pollution to these and other health problems.
ENC can help mitigate these negative effects by creating a quieter and more relaxing environment.
Versatile Applications
From headphones and smartphones to vehicles and home appliances, the applications of ENC are constantly expanding, improving comfort and quality of life in various settings.
Applications of ENC Technology
1. Headphones & Earbuds
ENC headphones are invaluable for travelers, students, and anyone working in noisy environments. They create a personal bubble of quiet, allowing for focused listening and reducing distractions.
2. Smartphones & Smart Speakers
Integrated ENC in smartphones and smart speakers improves call clarity and enhances voice recognition accuracy, even in challenging sound environments.
3. Vehicles
Many automobile manufacturers incorporate ENC to minimize engine and road noise, creating a more refined and comfortable driving experience.
4. Home Appliances
ENC technology in appliances like air conditioners and washing machines reduces operational noise, contributing to a quieter and more peaceful home.
Challenges and Limitations of Electronic Noise Cancellation
1. Ineffectiveness Against High-Frequency Sounds
ENC is most effective against consistent, low-frequency noises. It struggles to cancel sudden, high-frequency sounds like a dog bark or a door slam because these short-wavelength sounds change too rapidly for the real-time processing of ENC to effectively counteract.
2. Potential Impact on Audio Quality
While typically minimal, some ENC systems, especially feedback systems, can subtly alter the overall audio quality.
This is usually a trade-off for the noise reduction benefits.
3. Cost Considerations
Devices equipped with ENC technology are generally more expensive than their non-ENC counterparts due to the added components and complexity of the technology.
Future Trends in Noise Cancellation Technology
The future of ENC is bright, with ongoing research and development focusing on even smarter and more adaptive noise cancellation. These advancements include:
- AI-driven ENC: AI algorithms could personalize noise cancellation based on individual preferences and environmental conditions, dynamically adjusting to different sound profiles.
- Bone conduction ENC: This emerging technology could revolutionize communication in high-noise environments by transmitting sound through bone vibrations, bypassing the need for traditional speakers and microphones.
- Smart home integration: Future ENC systems could be integrated into smart homes, allowing for customized noise cancellation across entire rooms or even entire houses, creating truly personalized soundscapes.
Conclusion
Electronic noise cancellation has revolutionized how we experience sound in our daily lives.
By actively neutralizing unwanted noise, ENC technology creates quieter, more focused environments for work, leisure, and everything in between. From improving concentration and enhancing audio quality to promoting relaxation and protecting hearing health, the benefits of ENC are undeniable. As technology continues to advance, the future of ENC promises even more refined and personalized noise control, leading to quieter, more productive, and more peaceful environments for everyone.
If you haven’t experienced the transformative power of ENC, it’s time to discover the tranquility and focus a quieter world can offer.






